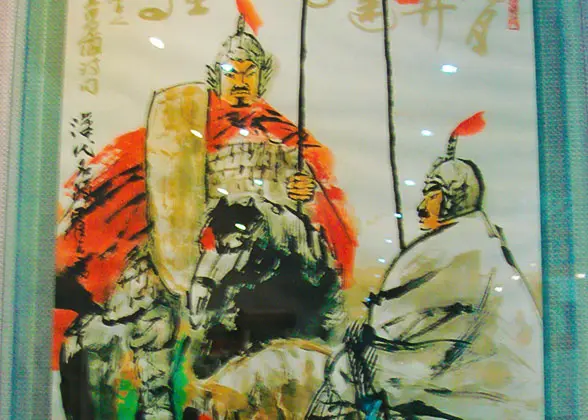
Wei Qing and Huo Qubing Beat Back the Huns
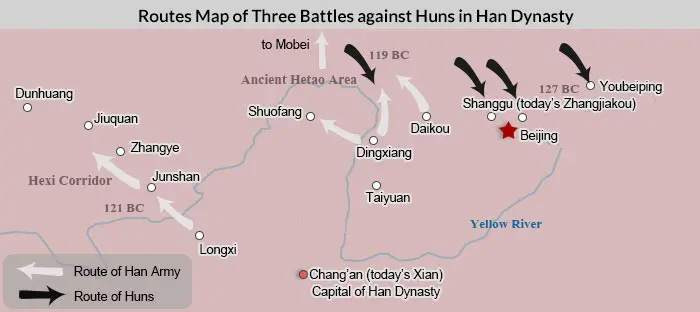
From 127 BC to 119 BC during the reign of Emperor Wu of the Han Dynasty, the famous generals Wei Qing and Huo Qubing launched three large-scale attacks against the Huns, also known as Xiongnu who disturbed the northern border of the Han Dynasty frequently, and finally expelled them far northwest of the Great Wall.
Why did Generals Wei Qing and Huo Qubing attack the Huns?
In the early Han Dynasty (202 BC - 220 AD), the Huns in the north were a big threat. They broke through the breaches of the Great Wall in disrepair every now and then and robbed the Han people. As the Han Court was newly founded and weak, the emperors used a relatively passive foreign policy, like marrying the princess to the Huns to change for short-time peace. When Emperor Wu ascended the throne in 141 BC, the Han court was strong enough to “fire a gun” at the Huns economically, politically, and militarily, so the foreign policy became offensive and the counterattack against the Huns started. Among the various attacks, those led by Generals Wei Qing and Huo Qubing are the most famous and effective.
|
|
Three Severe Attacks against Huns by Wei Qing and Huo Qubing
Battle of Henan
Henan, the ancient name for area around the 几-shaped bend of Yellow River, was in today's central Inner Mongolia. In 127 BC, the Huns invaded Huailai of Hebei Province in northeast China with their main military force. General Wei Qing did not fight with them face to face but used the opportunity to turn west and recapture the Henan area, where there was once the solid backup camp of the Huns.
Battle of Hexi
Hexi refers to the area including today's Dunhuang, Wuwei, Zhangye and Jiuquan of Gansu Province in west China. It is an important passage between the Han Court and the western regions. To recover the area occupied by the Huns, in the spring of 121 BC, General Huo Qubing led 10,000 elite cavalymen to attack the Hexi Corridor. He killed nearly 9,000 Huns and captured many of their aristocrats. In that summer, General Huo led troops to the north of Hexi Corridor and started the attack from northwest to southeast. The two sides had a severe fight near the Qilian Mountains. Finally, General Huo won and recaptured the Hexi Corridor.
Battle of Mobei
This is a long expedition of the Han army and one of the toughest battles the Han Court fought against the Huns. Although the previous battles attacked the Huns severely, they kept invading the northern border often, and then ran west for safety. They thought the Han army would never march far away north of the Great Wall, let alone go across the desert. This time, they were wrong! In 119 BC, Wei Qing and Huo Qubing led 50,000 cavalrymen respectively to march in west and east directions across the desert, reaching Mobei, the heart of Hun territory in today’s Mongolia. Although the severe battle brought great loss to the Han army, it weakened the Huns greatly and drove them to the far west. The battle brought peace to the Han border for many years.
 |
How did the Great Wall help Wei Qing and Huo Qubing attack the Huns?
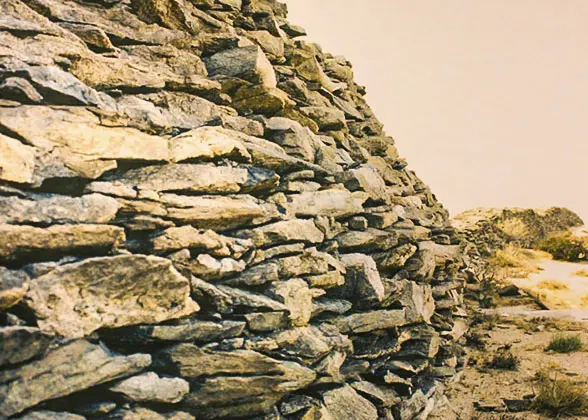
During the battles against the Huns, Wei Qing and Huo Qubing used the Great Wall as the base for attacks and retreats. After success, more sections were built to safeguard the recovered territories. For example, after the Battle of Henan, Emperor Wu set Shuofang and Wuyuan Prefectures there, restored the nearby fortresses built in Qin Dynasty (221 - 207 BC) and newly built the Shuofang Fortress. Also, after the Battle of Mobei, the Qin Dynasty Great Wall was restored and expanded in the west and north.
|
|
 Further Reading:
Further Reading:
→ Wei Qing (? – 106 BC) was a famous military general of the Western Han Dynasty (202 BC - 9 AD). Born in Linfen, Shanxi, he was the younger brother of Wei Zifu, the second empress of Emperor Wu.
→ Huo Qubing (140 – 117 BC) was the nephew of Wei Qing and also a famous general and strategist. He died at an early age of 24.
* The two generals’ tombs are one kilometer northeast of Emperor Wu's Maoling Mausoleum in Xi'an, Shaanxi. See Tomb of Huo Qubing.
Is it true that the defeat of Huns by Han Court led to the demise of the Western Roman Empire?
After the defeat of the Huns, some of them surrendered to the Han Court; some ran west. Those west-escaped Huns kept invaded other tribes and drove them even west, which led to the chaos of the far west countries, including the Western Roman Empire. Meanwhile, after accumulation of several generations, the Huns got strong again and started their expansion to the west, especially during the rule of Attila. Although Attila did not direct to the demise of the Western Roman Empire, he greatly weakened it, which was definitely one of the causes to its demise.
Famous Great Wall Battles:
![]() General Meng Tian Attacked the Huns in the North
General Meng Tian Attacked the Huns in the North
![]() Genghis Khan Breached China Great Wall
Genghis Khan Breached China Great Wall
![]() The War of Shanhaiguan Great Wall
The War of Shanhaiguan Great Wall
![]() Battle of Rehe - Last Battle on the Great Wall
Battle of Rehe - Last Battle on the Great Wall



