With rapid economic development in the country, China's railway capacity is persistently overtaken by demand. To meet the increasing demand, the authorities first increased the speed of trains to transport more passengers; then, high speed railways dedicated to
high speed trains were constructed.
Six Speedups - Support for Operation of High Speed Trains
 1997: The fast trains and overnight trains leaving in the evening and arriving in the morning were put into operation for the first time. The average speed of passenger trains was raised to 65 km/h (40.3 mph) from the previous 48 km/h (29.9 mph) of early 1993.
1997: The fast trains and overnight trains leaving in the evening and arriving in the morning were put into operation for the first time. The average speed of passenger trains was raised to 65 km/h (40.3 mph) from the previous 48 km/h (29.9 mph) of early 1993.
 1998: The top speed of fast trains was raised to 160 km/h (99 mph).
1998: The top speed of fast trains was raised to 160 km/h (99 mph).
 2000: The faster railway network reached about 10,000km (6,200 mi).
2000: The faster railway network reached about 10,000km (6,200 mi).
 2001: An additional 3,000km (1,850 mi) of railway were sped up.
2001: An additional 3,000km (1,850 mi) of railway were sped up.
 2004: Another 3,500 km (2,200 mi) of railway were sped up.
2004: Another 3,500 km (2,200 mi) of railway were sped up.
 2007: Intercity high speed trains started to run along improved rail tracks. Their top speed reached 250 km/h (155 mph).
2007: Intercity high speed trains started to run along improved rail tracks. Their top speed reached 250 km/h (155 mph).
| |  | | Spacious and Clean High Speed Carriage | |
Although the speed had been greatly raised and numerous fast trains had been put into service, the rail capacity still could not meet the demand. To deal with this, the plan of constructing a high speed railway network came into being, and the six nationwide China train speedups provided sound a technological foundation for the construction of high speed railways and operation of high speed trains.
Massive Construction of High Speed Railways
On August 1st, 2008, China's first high speed railway,
Beijing-Tianjin Intercity High Speed Railway was put into use, marking the beginning of the high speed era. Since then, high speed railways have been put into use one after another. By the end of 2023, the high speed rail tracks in China have reached
45,000 km (27,960 mi), accounting for about 2/3 of the world's high speed railroads. The high speed trains, also called bullet trains for their bullet-like locomotives, have been reached almost all large cities and most tourist cities in China.

See
China High Speed Railway Network Continuous Pursuing of Advanced High Speed Rail Technologies
The China train speed record is currently 486.1 km/h (302 mph) on existing track, 420 km/h (260 mph) on existing rail track for two pas trains and 605 km/h (375 mph) on test tracks, surpassing many countries in the world. Engineers are now working on maglev trains whose expected speed is 600 km/h (373 mph); high speed trains that can run in different countries with different gauges, different voltages, different environments and different signal control systems; and vacuum tube trains, also called super maglev which is said to be next phase in developing fast trains.
China High Speed Railways Go Abroad
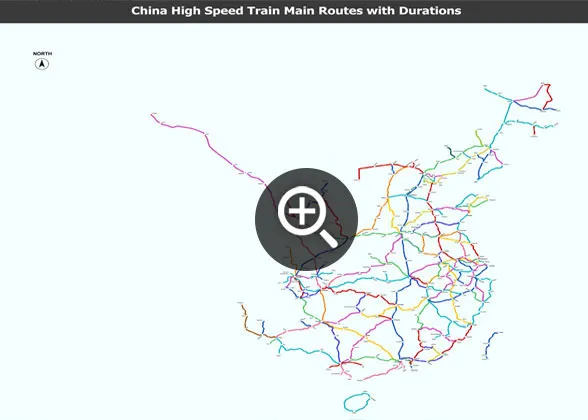 |
| China High Speed Railway Map |
|  Maps Maps
|
In addition to constructing high speed railroads in the country, China also plans to build several others to connect the country with its neighbors, including
China - Thailand Line,
China - Laos Line, and
China - Myanmar Line.
Also, the advanced high speed rail technologies have been approved by international markets. China is now helping to build high speed railways between Jakarta and Bandung in Indonesia, and between Medina and Mecca in Saudi Arabia. More overseas high speed rail projects are under negotiation or being planned. Meanwhile, high speed rail products also become popular worldwide. For instance, IGBT, similar to CPU of computers have been exported to India.
- Last updated on Aug. 06, 2025 by Grace Yang -
![]() 1997: The fast trains and overnight trains leaving in the evening and arriving in the morning were put into operation for the first time. The average speed of passenger trains was raised to 65 km/h (40.3 mph) from the previous 48 km/h (29.9 mph) of early 1993.
1997: The fast trains and overnight trains leaving in the evening and arriving in the morning were put into operation for the first time. The average speed of passenger trains was raised to 65 km/h (40.3 mph) from the previous 48 km/h (29.9 mph) of early 1993.![]() 1998: The top speed of fast trains was raised to 160 km/h (99 mph).
1998: The top speed of fast trains was raised to 160 km/h (99 mph).![]() 2000: The faster railway network reached about 10,000km (6,200 mi).
2000: The faster railway network reached about 10,000km (6,200 mi).![]() 2001: An additional 3,000km (1,850 mi) of railway were sped up.
2001: An additional 3,000km (1,850 mi) of railway were sped up.![]() 2004: Another 3,500 km (2,200 mi) of railway were sped up.
2004: Another 3,500 km (2,200 mi) of railway were sped up.![]() 2007: Intercity high speed trains started to run along improved rail tracks. Their top speed reached 250 km/h (155 mph).
2007: Intercity high speed trains started to run along improved rail tracks. Their top speed reached 250 km/h (155 mph).

